8. Crosscutting Concepts
Content
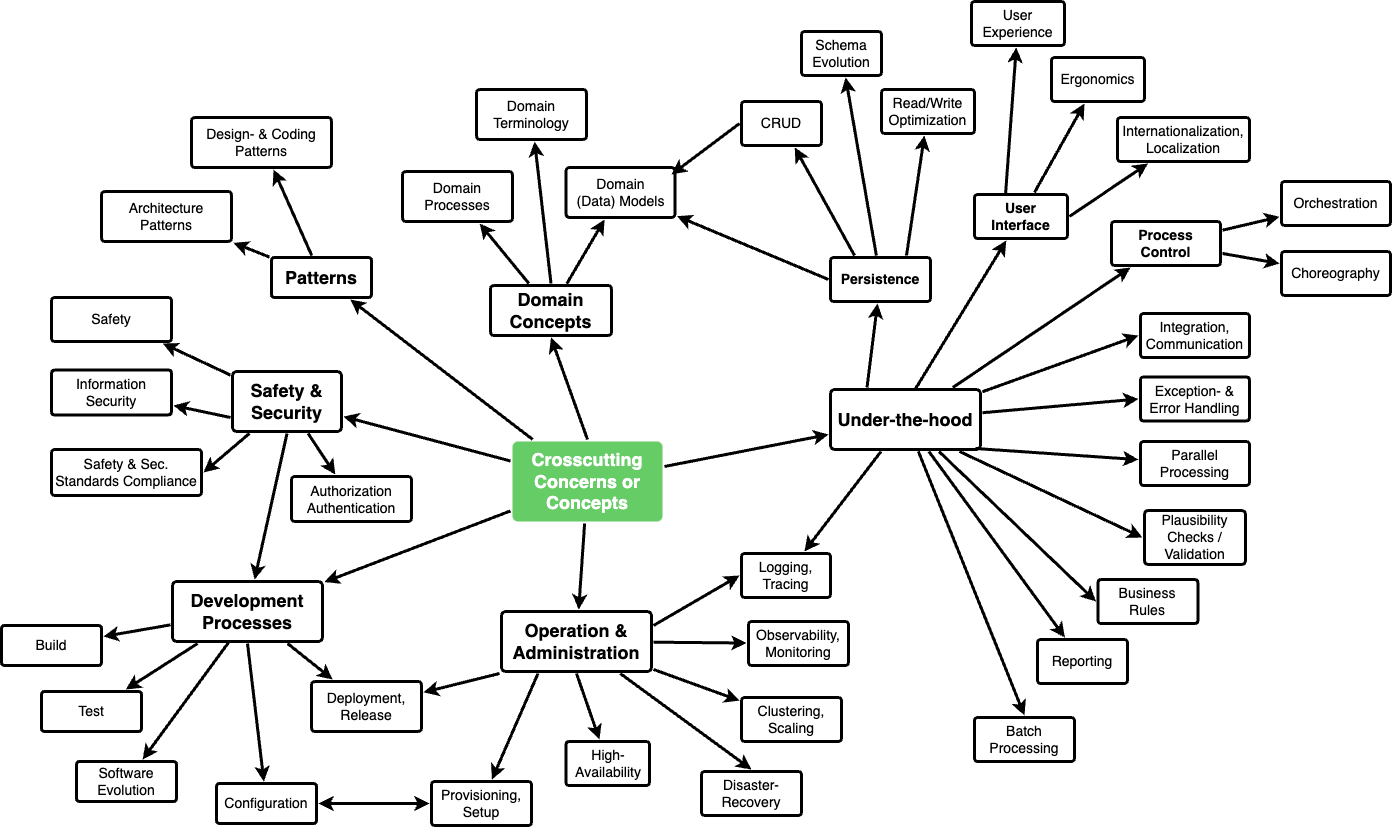
This section describes crosscutting concepts (practices, patterns, regulations or solution ideas). Such concepts are often related to multiple building blocks. They may include many different topics, such as the topics shown in the following diagram:
Motivation
Concepts form the basis for conceptual integrity (consistency, homogeneity) of the architecture. Thus, they are an important contribution to achieve inner qualities of your system.
This is the place in the template that we provided for a cohesive specification of such concepts.
Many of these concepts relate to or influence several of your building blocks.
Form
The form can be varied:
- concept papers with any kind of structure
- example implementations,especially for technical concepts
- cross-cutting model excerpts or scenarios using notations of the architecture views
Structure of this section
Pick only the most-needed topics for your system and assign each a level-2 heading in this section (e.g. 8.1, 8.2 etc).
DO NOT ATTEMPT to cover all of the topics of the aforementioned diagram.
Background
Some topics within systems often concern multiple building blocks, hardware elements or development processes. It might be easier to communicate or document such cross-cutting topics at a central location, instead of repeating them in the description of the concerned building blocks, hardware elements or development processes.
Certain concepts might concern all elements of a system, others might only be relevant for a few. In the diagram above, logging concerns all three components, whereas security is relevant only for two components.
Some real-life examples:
- Within a system, a common format for log-messages shall be established, combined with a common convention of choosing the appropriate log-destination. These decisions, along with implementation examples, could be described as “logging-concept”.
- A system has numerous backend services, that communicate among each other based upon remote procedure calls or https-based REST.
- Calling services (“consumers”) always need to authenticate themselves to the called service (“provider”).
- For this authentication, a central common authorization service has to be used.
- The technical and organizational details such authentication could be described as “backend authentication concept”.
- (taken from the HTML Sanity Checker, see below): All (7+) checker components within the system are structured according to the strategy pattern.
Examples
<describe concepts here >
Further Info
Tips
Related Questions
See here for questions related to crosscutting and/or technical concepts.
